Why Your Blood Sugar Spikes After Eating (Even Without Diabetes) Expert Reveals Secrets
Even if you don’t have diabetes, your blood sugar may be the cause if you’ve ever felt lethargic, jittery, or unusually full after eating and wondered what’s going on. Postprandial (after-meal) blood sugar spikes are not only a problem for diabetics, according to recent research and professional opinions. To improve your metabolic health, you must first understand why they can affect anyone.
Blood Sugar Spikes Aren’t Just a Diabetic Concern
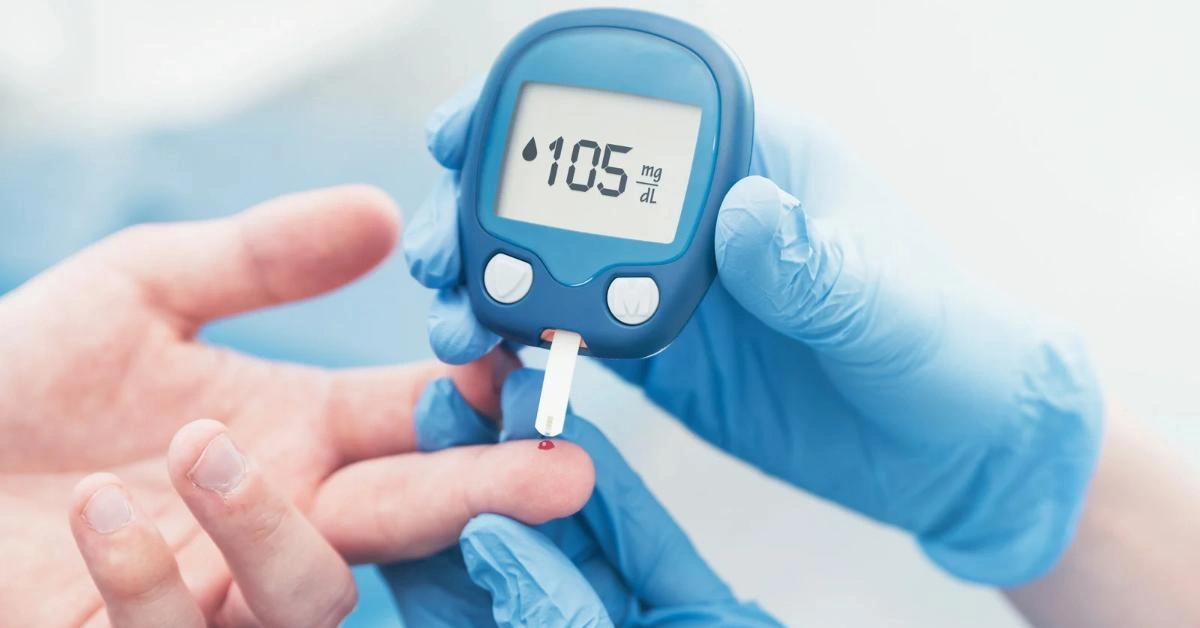
It’s common for our blood glucose levels to increase after eating, particularly when we consume foods high in carbohydrates. However, even in those without insulin resistance or a diagnosis of diabetes, the spike is more severe and lasts longer. “Depending on what and how you eat, blood sugar can spike significantly even in non-diabetics,” says endocrinologist and metabolic health researcher Dr. Stephanie Wallis, MD. “These frequent spikes in blood sugar may eventually raise the risk of cardiovascular problems, weight gain, and inflammation.”
What the Latest Research Shows
Up to 80% of individuals without diabetes experience post-meal glucose spikes exceeding 140 mg/dL, which is generally regarded as the upper limit of normal, according to a 2023 study published in Cell Metabolism. Researchers monitored participants’ continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and found that blood sugar response is influenced by sleep, gut microbiome diversity, meal timing, and even meal composition. These results were supported by another Harvard Health article, which pointed out that, independent of preexisting health conditions, processed carbohydrates, sugar-filled drinks, and sedentary lifestyles are major contributors to glucose variability. The original research is available here.
Why These Spikes Matter for Your Health
Even a small spike in blood sugar can cause mood swings, cravings, energy crashes, and eventually metabolic syndrome or prediabetes. Over 96 million adults in the United States have prediabetes, and many are unaware of it, according to the CDC. According to registered dietitian Dr. Lisa Harper, RD, who specializes in metabolic health, “chronically unstable glucose levels stress your pancreas and insulin production.” “You might be headed toward insulin resistance without even being aware of it if you don’t have diabetes.”
How to Prevent Blood Sugar Spikes After Eating
The good news? You don’t need to overhaul your entire diet just make smarter, science-backed choices. Here are expert-recommended tips:
1. Eat in the Right Order
Vegetables high in fiber should be eaten first, then proteins and good fats. Put the carbohydrates last. This moderates your blood sugar response and slows the absorption of glucose.
2. Don’t Skip Movement
A 10-minute walk after meals can help reduce postprandial glucose spikes by improving insulin sensitivity, according to the NIH.
3. Prioritize Whole Foods
Limit sugar and refined carbohydrates. Select complex carbohydrates that stabilize energy levels and digest slowly, such as sweet potatoes, lentils, or quinoa.
4. Stay Hydrated
Water consumption aids in the kidneys’ removal of extra glucose. Unless your healthcare provider instructs you otherwise, try to consume at least 8 cups per day.
5. Consider a CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitor)
Some people use CGMs (under medical supervision) to monitor how their bodies respond to various foods even if they do not have diabetes. You can customize your diet with the help of this biofeedback.
Awareness is Your First Line of Defense
Blood sugar control is important even if you don’t have diabetes. You can feel more energized, control your weight more skillfully, and lower your long-term risk of metabolic disease by identifying and treating post-meal glucose spikes. According to Dr. Wallis, “metabolic health is a spectrum.” “We are better prepared to prevent chronic illness the sooner we pay attention to our body’s subtle glucose cues.” Consult a healthcare professional if you’re having symptoms like extreme cravings for carbohydrates, brain fog, or fatigue after meals. Better results come from early awareness, and frequently all you need to do is make small lifestyle changes.
Check out the healthlynic ✔️approved range of products for Weight Loss, Improve metabolism and much more!