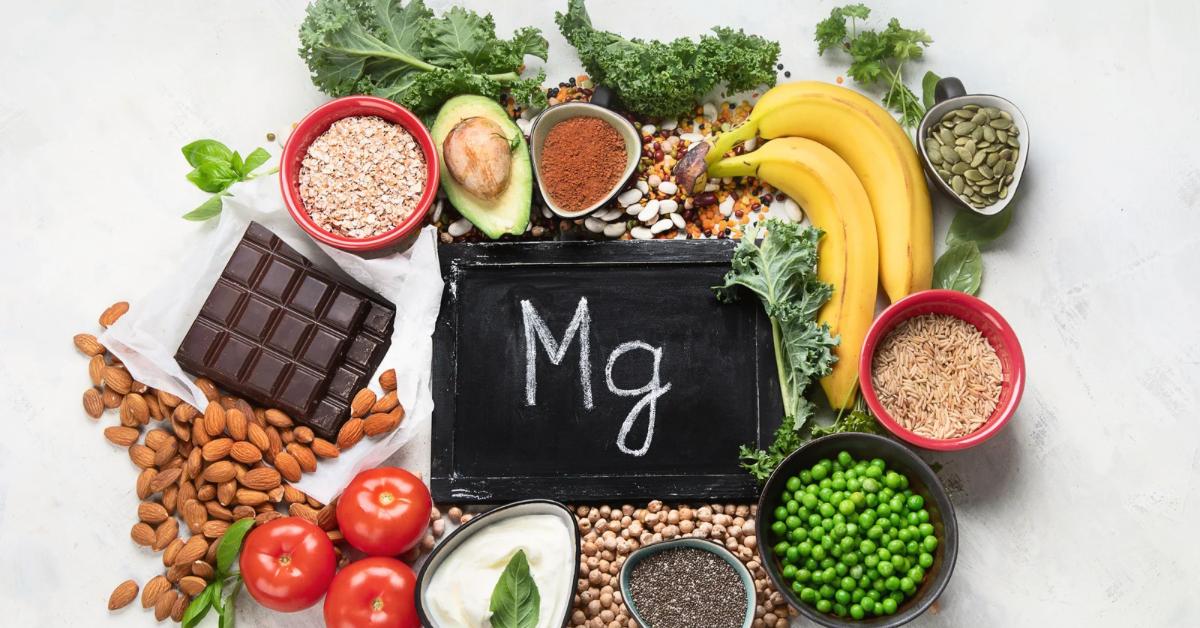Low Magnesium? These 8 Symptoms Might Be Warning You
Have you recently experienced unusually high levels of anxiety, twitches, or fatigue? Something as basic and necessary as low magnesium levels could be the cause. Despite being frequently disregarded, magnesium is essential for more than 300 enzymatic processes in the body, ranging from nerve function to energy production and muscle relaxation. Experts are now warning that magnesium deficiency affects almost 50% of Americans and is more common than we realize. Until symptoms appear, there are frequently no outward signs of the condition.
What Experts Say About Magnesium Deficiency
According to internal medicine specialist and Minerals That Matter author Dr. Karen Fields, MD, “magnesium is like the body’s electrical current—it keeps everything running smoothly.” “Symptoms of a drop in your levels may be mild at first, but if untreated, they may worsen.” “We’re seeing more magnesium deficiency due to poor soil quality, highly processed diets, and chronic stress, all of which deplete magnesium faster than we can replenish it,” said Dr. Julian Moreno, a registered dietitian and expert in functional nutrition.
8 Common Signs of Low Magnesium
Wondering if your body might be running low? Here are eight symptoms of magnesium deficiency to watch for:
- Muscle Cramps or Spasms
Involuntary muscle twitches especially in the legs are one of the most recognized signs of low magnesium. - Fatigue or Weakness
Magnesium is essential for ATP (energy) production. Deficiency may leave you feeling drained, even after a full night’s sleep. - Irritability, Anxiety, or Mood Swings
Magnesium helps regulate neurotransmitters that affect mood. Low levels have been linked to increased anxiety and even depression. - Insomnia or Trouble Staying Asleep
Without enough magnesium, your nervous system can stay in “fight or flight” mode, making it harder to relax and fall asleep. - Irregular Heartbeat (Palpitations)
Magnesium helps maintain a steady heart rhythm. Deficiency may cause skipped beats or rapid heart rate. - Frequent Headaches or Migraines
Several studies suggest that low magnesium is a trigger for migraines and tension-type headaches. - Numbness or Tingling
Low magnesium can affect nerve conduction, leading to tingling sensations in the extremities. - Constipation
Magnesium helps relax the digestive muscles. Deficiency may lead to sluggish bowel movements and bloating.
What the Research Shows
According to a 2023 study published in the Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 48% of Americans—particularly women and older adults—consume less magnesium than is advised daily. Low serum magnesium was also associated in the study with a higher risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes. Another peer-reviewed article in Nutrients (2022) emphasized that chronic low magnesium can worsen insulin resistance, elevate blood pressure, and increase inflammatory markers in the body.
For detailed research, visit the NIH Office of Dietary Supplements.
Why Magnesium Deficiency Is a Public Health Concern
Despite being a component of almost every bodily system, magnesium is rarely examined in standard laboratory procedures. Accordingly, magnesium deficiency is a “silent epidemic” that, if disregarded, can have a serious negative influence on long-term health. The CDC states that poor diet quality continues to be a major cause of chronic diseases, many of which are impacted by magnesium status, such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension. According to Dr. Fields, “magnesium is no longer optional.” It is fundamental. You’re building your health on shaky foundations without it.
How to Boost Magnesium Levels Naturally
You can correct mild to moderate magnesium deficiency with simple lifestyle changes:
1. Eat Magnesium-Rich Foods
Prioritize whole foods like:
- Leafy greens (spinach, Swiss chard)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, pumpkin seeds)
- Legumes (black beans, lentils)
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa)
- Dark chocolate (at least 70% cocoa)
2. Limit Sugar and Processed Foods
These deplete magnesium and provide little in return.
3. Stay Hydrated
Magnesium is lost through urine. Drink plenty of water especially if you consume caffeine or alcohol.
4. Consider a Supplement
For adults, 310–420 mg per day is the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA). A magnesium citrate or glycinate supplement might be helpful if you’re not getting that from food. Before beginning a supplement regimen, always get medical advice.
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress increases magnesium excretion. Incorporate relaxation practices like yoga, breathwork, or nature walks to preserve your levels.
Final Thoughts: Don’t Overlook This Essential Mineral
Checking your magnesium levels may be necessary if you’re feeling strange, such as having frequent cramps, low energy, or anxiety. The long-term consequences of a deficiency are not as subtle as the symptoms. The good news? With dietary changes and more intelligent lifestyle choices, the majority of cases can be easily resolved. According to Dr. Moreno, “magnesium is one of the most effective, low-risk ways to support your health.” “Do not consider it an afterthought, but a daily necessity.”
Check out the healthlynic ✔️approved range of products for Weight Loss, Improve metabolism and much more!